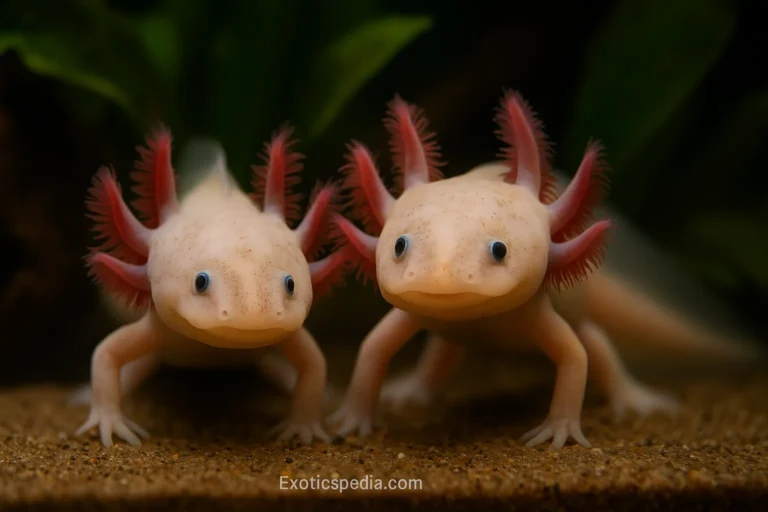
The Xochimilco Crisis: Habitat Engineering and the Axolotl’s Last Stand
Jab hum Ambystoma mexicanum ki baat karte hain, toh aksar unke regenerative powers par tawajjo di jati hai. Magar ecological perspective se, axolotl is waqt duniya ke sabse bade “Conservation Crisis” ka samna kar raha hai. Inka natural habitat—Lake Xochimilco ka ancient canal system—tezi se khatam ho raha hai, jis se ye species wild mein extinction ke qareeb pahunch chuki hai.
Lake Xochimilco: The Last Bastion of the Axolotl
Lake Xochimilco sirf ek pani ka zariya nahi hai, balki ek complex artificial ecosystem hai jo Aztec daur mein banaya gaya tha. Inhein “Chinampas” (floating gardens) kaha jata hai.
- Niche Ecology: Axolotls in canals ke thanday aur stagnant pani mein rehte hain jahan oxygen levels aur temperature unki neotenic biology ke liye perfect hota hai.
- The Transition: Pichle 50 saalon mein, Mexico City ki urbanization ne is jannat ko ek “Ecological Sink” mein badal diya hai.
Anthropogenic Pressures: Why the Wild Population is Plummeting
Axolotl ki wild population 1998 mein 6,000 per square kilometer thi, jo ab gir kar shayad 35 per square kilometer se bhi kam reh gayi hai. Iski wajah teen bade factors hain:
1. Invasive Species: The Tilapia and Carp Problem
1970s aur 80s mein, food security ke liye Lake Xochimilco mein African Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) aur Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) chhodi gayi thi.
- Predation: Ye invasive machhliyan na sirf axolotls ke eggs aur larvae ko khati hain, balki unke food sources (crustaceans) ke liye bhi muqabla karti hain.
- The Impact: Axolotl ka regeneration mechanism unhein predation se nahi bacha sakta jab poora ka poora larva hi nigal liya jaye.
2. Eutrophication and Water Toxicity
Mexico City ka sewage aur industrial runoff canals mein shamil ho raha hai. Is se pani mein nitrogen aur phosphorus barh jata hai (Eutrophication), jo algae blooms paida karta hai. Ye algae pani se oxygen kheench lete hain, jis se axolotls ke feathery gills (branchial arches) suffocated ho jate hain.
The “Chinampa Refugio” Project: A Symbiotic Recovery Model
Sabse bada Information Gain is waqt Chinampa Refugio project hai. Ye project UNAM (National Autonomous University of Mexico) ke researchers ne shuru kiya hai.
- Habitat Engineering: Researchers ne canals ke dahanon par filter lagaye hain jo invasive Tilapia ko bahar rakhte hain.
- Traditional Agriculture: Chinampero (farmers) ko encourage kiya ja raha hai ke wo chemicals ke bajaye organic farming karein.
- The Result: Ye “refugios” ek aisi safe zone banate hain jahan wild axolotls baghair kisi khatre ke breed kar sakte hain.
Genetic Bottlenecks: Wild vs. Captive Diversity
Ek bada khatra jo scientists mehsoos karte hain wo hai Genetic Drift.
- Duniya bhar ki labs aur pet stores mein lakhon axolotls hain, magar wo sab sirf kuch hi purkhon (ancestors) ki aulad hain.
- Wild population ki genetic diversity khatam hone ka matlab hai ke species ki bemariyon se larne ki taqat khatam ho jayegi. Isliye wild population ki axolotl conservation sirf ek janwar bachana nahi, balki unka original DNA bachana hai.